Manufacturing rate continues its decline as demand slows
Economic Update
For July, the U.S. manufacturing rate was 46.8% on the ISM Index, a decline of 1.7% from the previous month. Any reading under 50.0% is contractionary, marking four consecutive months of declines. Elevated interest rates and inflation are pushing manufacturing activity deeper into contraction, with demand remaining subdued as companies show an unwillingness to invest capital and inventory. The unemployment rate increased to 4.3% in July, adding 114,000 jobs, a sharp slowdown from June when payrolls grew by 206,000 jobs. The cooldown in the labor market should position the fed to begin easing monetary policy in September.
State of Corporate Credit
Default risk remains high for “Risky Credits”, which are defined as companies rated “B-“ or lower by S&P. Risky Credits in North America fell by 8.2% in Q1 2024. This statistic would generally be viewed positively, but 42% of total risky credit removals were caused by companies defaulting in the first quarter. Form Technologies, Inc. was downgraded to ‘CCC+’ in December as its $900 billion in debt matures in 2025. Wheel Pros, Inc. was recently downgraded to ‘CC’ after missing interest payments which increases the likelihood of a distressed debt restructuring.
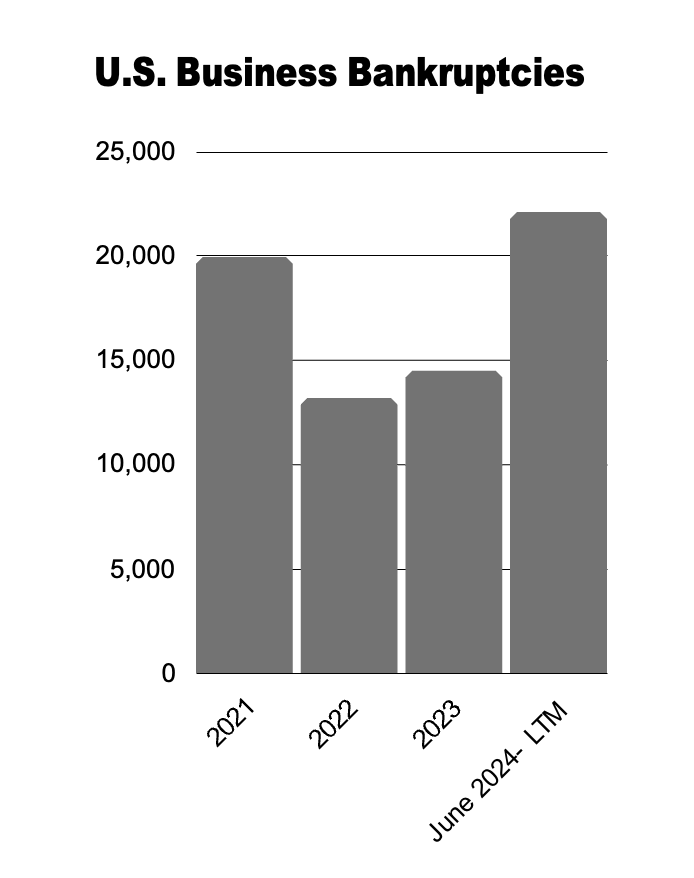
Insolvencies
Commercial Chapter 11 filings increased by 40% in July 2024 when compared to July 2023. The continued strong and steady rise in bankruptcy filings reflects the ongoing financial pressures faced by businesses. Headwinds include increased costs, elevated interest rates, slowing demand, and geopolitical tensions. The steady increase in filings is expected to continue throughout the remainder of 2024 and into 2025. In Canada, business insolvencies surged by 41.4% when compared to last year.
Current & Evolving Credit Risks
Slowing Demand
Manufacturing companies are bracing for an extended slump in demand, after posting record profits following the post-Covid manufacturing boom. Makers of automobiles, crop-harvesting combines, and washing machines project challenging business conditions. This translates into lower demand for steel and lower purchase volumes, as buyers expect that prices will continue to fall. Weak demand for steel has caused the price to decline to $655 a ton (as of July 29), which is down 22% from a year ago and 40% from the beginning of the year. This will negatively impact revenue and margins, and credit metrics will turn negative for high-cost producers if pricing weakens beyond their cash costs.
Solar Industry Troubles
The solar industry, which experienced a decade of exponential growth, faced immense challenges in 2023. Higher interest rates, tighter financing, and adverse policy shifts led to over 100 solar bankruptcies for the year, with the trend being similar in 2024. In California alone, these factors led to an 80% decrease in rooftop solar installation volume. The risk in the industry is expected to continue for the year, as economic headwinds persist.